Character LCD Display Interface
TM4C123GH6PMComplete Lab Manual
For the complete experiment including learning objectives, theoretical background, and detailed explanations, download the PDF manual: Download Experiment 7 PDF
Examples
Example: Basic LCD Driver Implementation
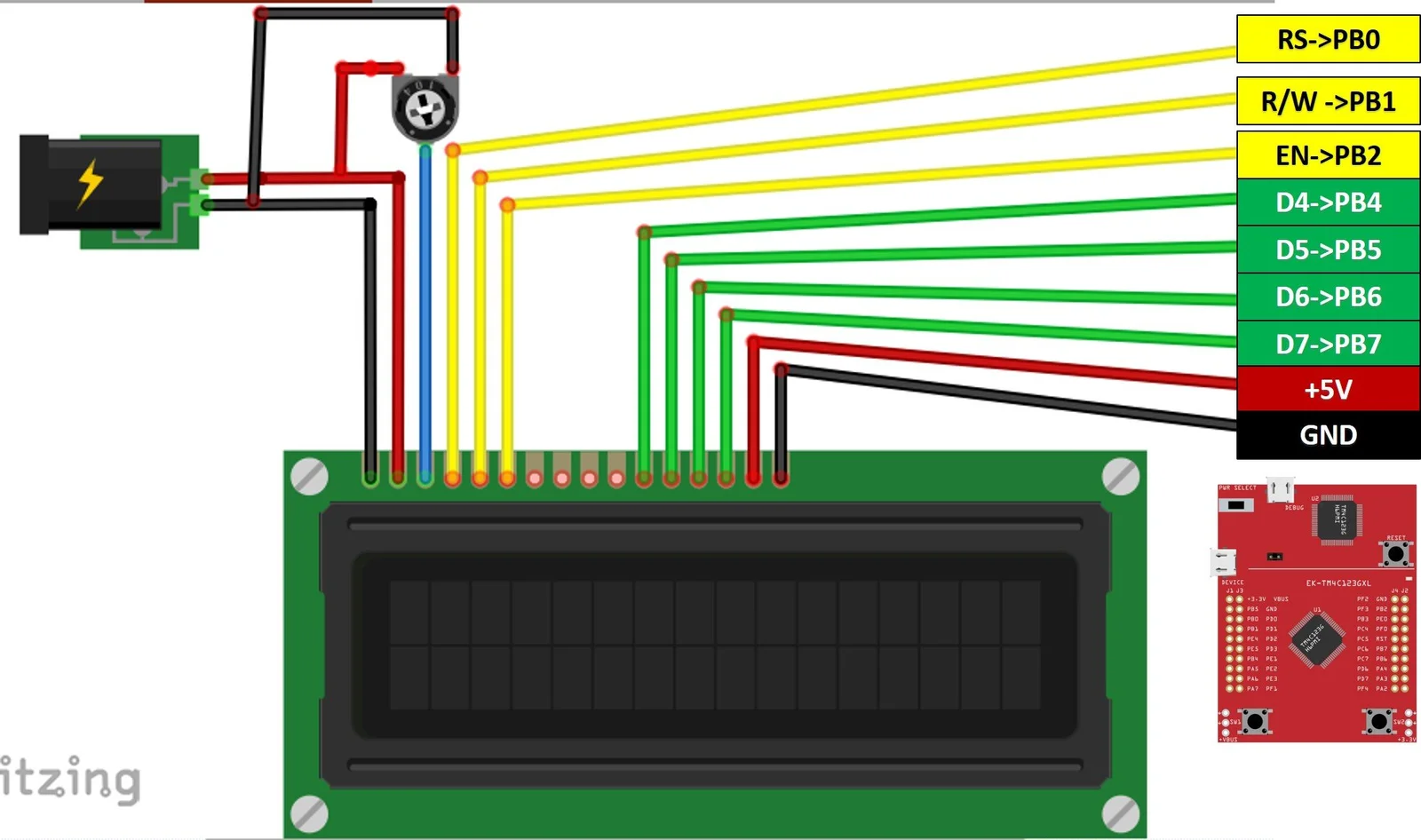
The figure above shows the complete wiring diagram for connecting the 16×2 LCD module to the TM4C123 microcontroller using 4-bit mode. The connections are:
- Power: VDD to VBus, VSS to Ground, V0 to contrast potentiometer
- Control: RS to PB0, E to PB2, RW to Ground (write-only)
- Data: D4-D7 to PB4-PB7 respectively
- Backlight: A to VBus, K to Ground
The contrast potentiometer (typically 10kΩ) allows adjustment of the display visibility - rotating it changes the voltage on V0 pin between 0V and VDD.
The following code demonstrates a complete LCD driver in 4-bit mode with initialization, command/data transmission, and text display functions.
#ifndef LCD_H
#define LCD_H
#include "TM4C123.h"
// LCD pin definitions (connected to PORTB)
#define RS (1 << 0) // PB0
#define RW (1 << 1) // PB1
#define EN (1 << 2) // PB2
#define DATA_MASK 0xF0 // PB4-PB7
// Function prototypes
void LCD_Init(void);
void LCD_Command(unsigned char cmd);
void LCD_Data(unsigned char data);
void LCD_Clear(void);
void LCD_SetCursor(unsigned char row, unsigned char col);
void LCD_Print(char *str);
void delay_us(int us);
void delay_ms(int ms);
#endif#include "lcd.h"
#define CYCLES_PER_US (SystemCoreClock / 1000000u)
//====================[ SysTick Delay Functions ]====================
void SysTick_Init(void)
{
SysTick->CTRL = 0;
SysTick->LOAD = CYCLES_PER_US - 1; // 1us delay at 50MHz
SysTick->VAL = 0;
SysTick->CTRL = 0x5; // Enable with system clock
}
void delay_us(int us)
{
SysTick->LOAD = (CYCLES_PER_US * us) - 1;
SysTick->VAL = 0;
SysTick->CTRL = 0x5; // Enable with system clock
while ((SysTick->CTRL & 0x10000) == 0);
SysTick->CTRL = 0;
}
void delay_ms(int ms)
{
while (ms--)
delay_us(1000);
}
//====================[ LCD Helper Functions ]====================
void LCD_EnablePulse(void)
{
delay_us(1);
GPIOB->DATA |= EN;
delay_us(1);
GPIOB->DATA &= ~EN;
delay_us(1);
}
void LCD_SendNibble(unsigned char nibble)
{
// Send nibble to PB4-PB7
GPIOB->DATA = (GPIOB->DATA & ~DATA_MASK) | ((nibble << 4) & DATA_MASK);
LCD_EnablePulse();
}
//====================[ LCD Initialization ]====================
void LCD_Init(void)
{
// Enable clock to PORTB
SYSCTL->RCGCGPIO |= (1 << 1);
while ((SYSCTL->PRGPIO & (1 << 1)) == 0)
;
// Configure PB0 (RS), PB1 (EN), PB4-PB7 (data) as output
GPIOB->DIR |= RS | RW | EN | DATA_MASK;
GPIOB->DEN |= RS | RW | EN | DATA_MASK;
GPIOB->DATA &= ~(RS | RW | EN | DATA_MASK); // Clear all
SysTick_Init();
delay_ms(50); // Wait for LCD to power up
// Initialization sequence (8-bit interface mode to start)
LCD_SendNibble(0x03);
delay_ms(5);
LCD_SendNibble(0x03);
delay_us(150);
LCD_SendNibble(0x03);
delay_us(150);
LCD_SendNibble(0x02); // Set 4-bit mode
delay_us(150);
// Now in 4-bit mode: use full commands
LCD_Command(0x28); // Function set: 4-bit, 2 lines, 5x8 dots
LCD_Command(0x0C); // Display ON, Cursor OFF
LCD_Command(0x06); // Entry mode: increment cursor
LCD_Command(0x01); // Clear display
delay_ms(2);
}
//====================[ LCD Command/Data API ]====================
void LCD_Command(unsigned char command)
{
GPIOB->DATA &= ~RS; // RS = 0 for command
delay_us(1);
LCD_SendNibble(command >> 4); // Upper nibble
LCD_SendNibble(command & 0x0F); // Lower nibble
delay_ms(2);
}
void LCD_Data(unsigned char data)
{
GPIOB->DATA |= RS; // RS = 1 for data
delay_us(1);
LCD_SendNibble(data >> 4);
LCD_SendNibble(data & 0x0F);
delay_ms(1);
}
void LCD_Clear(void)
{
LCD_Command(0x01);
delay_ms(2);
}
void LCD_SetCursor(unsigned char row, unsigned char col)
{
unsigned char address = (row == 0) ? 0x80 + col : 0xC0 + col;
LCD_Command(address);
delay_ms(1);
}
void LCD_Print(char *str)
{
while (*str)
{
LCD_Data(*str++);
}
}
#include "TM4C123.h"
#include "lcd.h"
int main(void)
{
LCD_Init();
LCD_Clear(); // Ensure display is clear
LCD_SetCursor(0,0); // Set cursor to beginning
LCD_Print("ENCS4110 Lab");
while(1)
{
}
}Code Explanation
Initialization Sequence
The LCD_Init() function implements the complete 4-bit initialization:
- Enables GPIO PORTB clock and configures pins as outputs
- Waits 50 ms for LCD power-on stabilization
- Sends
0x03(upper nibble) three times with delays (8-bit mode reset) - Sends
0x02(upper nibble) to switch to 4-bit mode - Sends configuration commands:
0x28(4-bit, 2 lines),0x0C(display on),0x06(entry mode),0x01(clear)
Nibble Transmission
The LCD_SendNibble() function:
- Masks out current data bits (PB4-PB7)
- Places the 4-bit nibble on PB4-PB7 (shifted left by 4)
- Generates enable pulse: delay → E high → delay → E low → delay
Command vs. Data
LCD_Command(): Sets RS=0, sends upper nibble, sends lower nibbleLCD_Data(): Sets RS=1, sends upper nibble, sends lower nibble
Cursor Positioning
The LCD_SetCursor(row, col) function calculates the DDRAM address:
address = (row == 0) ? 0x80 + col : 0xC0 + col;Then sends the address as a command.
String Printing
The LCD_Print(str) function iterates through the string and sends each character using LCD_Data().
Tasks
Task 1: Display Your Name and ID
Update the main program to display your name on the first line and your student ID on the second line of the LCD.
Requirements:
- Clear the display
- Set cursor to line 1, column 0
- Print your name (up to 16 characters)
- Set cursor to line 2, column 0
- Print your student ID
Hint:
LCD_Clear();
LCD_SetCursor(0, 0); // Line 1
LCD_Print("Your Name");
LCD_SetCursor(1, 0); // Line 2
LCD_Print("ID: 1234567");Task 2: Button-Controlled Name Scrolling
Write a program that displays your name on the LCD and allows the user to scroll the text left or right using the two on-board push buttons (SW1 and SW2).
Requirements:
- Display your name on line 1
- Configure SW1 (PF4) and SW2 (PF0) with GPIO interrupts (falling edge, internal pull-up)
- When SW1 is pressed: Shift display left (command
0x18) - When SW2 is pressed: Shift display right (command
0x1C) - The display should not scroll automatically; only respond to button presses
Task 3: Bidirectional Continuous Scrolling
Write a program that displays your name on line 1 and your student ID on line 2, with continuous scrolling in opposite directions after a button press.
Requirements:
- Display your name on line 1 and ID on line 2
- Initially, the display is static (no scrolling)
- When SW1 is pressed, start continuous scrolling:
- Line 1 scrolls right
- Line 2 scrolls left
- Pressing SW1 again stops the scrolling
- Use a timer interrupt to handle the scrolling at a fixed interval (e.g., every 500 ms)